Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) have revolutionized the way we track and manage assets, personnel, and resources in diverse industries. This technology, which offers precise location tracking in real-time, has become a cornerstone in the landscape of modern operational management and strategic planning. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of RTLS, exploring its various components, applications, and the significant impact it has on industries ranging from healthcare to logistics.
We begin by defining RTLS, outlining its key features, and discussing why it is increasingly critical in today’s fast-paced, data-driven world. Following this, the article will guide you through the different types of RTLS technologies available, their respective advantages, and practical scenarios where they can be applied. In addition to highlighting the technological aspects, we will also address the challenges and considerations in implementing RTLS solutions, offering insights from industry experts and case studies. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how RTLS works, its transformative potential, and how it can be harnessed to optimize operations and enhance decision-making processes in various sectors. Join us on this journey to uncover the dynamic world of Real-Time Location Tracking Technology and its pivotal role in shaping the future of industry and technology.
Understanding RTLS Technology
Delving deeper into the mechanics of Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS), we find that this technology is not just about locating objects or individuals; it’s about doing so with precision and speed, often in complex environments. At its core, RTLS operates by utilizing a network of wireless devices that communicate with tags attached to the objects or individuals to be tracked. These tags transmit signals, which are then processed to determine their location, typically in real-time. This section of the article will explore the key technologies that make RTLS both versatile and powerful.
Firstly, Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) is a foundational technology in many RTLS setups. Using electromagnetic fields, RFID tags, which can be passive or active, communicate their identity and other data to RFID readers. This technology is instrumental in inventory management and asset tracking due to its range and reliability. It is common to see RTLS deployments integrate RFID solutions for a single source of location insights.
Next, we delve into Wi-Fi-based RTLS, which utilizes existing Wi-Fi networks to locate devices. This cost-effective and easily scalable approach makes it ideal for indoor environments like offices or hospitals. Similarly, Bluetooth, especially in its Low Energy (BLE) iteration, has emerged as a popular RTLS technology. BLE is renowned for its low power consumption and has been instrumental in developing proximity-based applications, such as contact tracing apps during the COVID-19 pandemic. The latest BLE technologies rival competing technologies like ultra-wideband (UWB) for their location accuracy.
Finally, the integration of RTLS with the Internet of Things (IoT) creates a synergy that amplifies the capabilities of both. By connecting RTLS-enabled devices to the IoT network, data collected from these devices can be analyzed and used to optimize processes, predict maintenance needs, and enhance overall operational efficiency. This integration is paving the way for smart factories, automated warehouses, and advanced healthcare monitoring systems, underlining the transformative potential of RTLS when combined with IoT.
In summary, understanding the various technologies underpinning RTLS and their integration with IoT is crucial to appreciating the system’s full potential and the breadth of its applications. This comprehensive overview sets the stage for a deeper exploration of specific RTLS use cases and benefits in subsequent sections of the article.
RTLS in Healthcare
Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) in healthcare mark a significant leap in managing and optimizing hospital operations, patient care, and staff safety. In the complex and dynamic environment of healthcare facilities, RTLS technology plays a crucial role in ensuring efficiency, security, and quality of care. This segment will delve into the multifaceted impact of RTLS in healthcare, highlighting its applications, benefits, and future trends.
RTLS technology in healthcare primarily focuses on asset tracking and management. In a sector where timely access to medical equipment can be critical, RTLS helps in real-time monitoring of assets like wheelchairs, defibrillators, and infusion pumps. This tracking not only reduces the time staff spend searching for equipment but also significantly cuts down on the costs associated with lost or misplaced assets. Case studies from various hospitals reveal dramatic asset utilization rate improvements and procurement expense reductions. For instance, a study by ‘HIMSS’ demonstrated how the implementation of RTLS reduced the time spent by nurses in locating equipment, thereby enhancing patient care efficiency.

Another crucial application of RTLS in healthcare is enhancing personnel safety. Airista Flow, offers solutions that ensure the safety of healthcare workers in potential situations of workplace violence or emergencies. Their RTLS badges enable immediate location tracking of staff during emergencies, delivering messages to responders’ tags allowing rapid response, and ensuring staff security. This application has become particularly relevant in light of increasing concerns about healthcare worker safety. The AiRISTA staff safety solution works over both Wi-Fi and BLE for network redundancy and supports 2-way messaging for a coordinated response. https://www.airistaflow.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/image.png
Looking towards the future, RTLS in healthcare is poised for significant growth and innovation. Predictions suggest a trend towards more integrated systems, combining RTLS with other technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to provide predictive analytics. This integration could lead to smarter resource allocation, improved patient flow management, and enhanced preventive maintenance of medical equipment. AiRISTA’s RTLS software platform, Sofia, is ready as a streaming broker-based architecture written in the language “Go”.
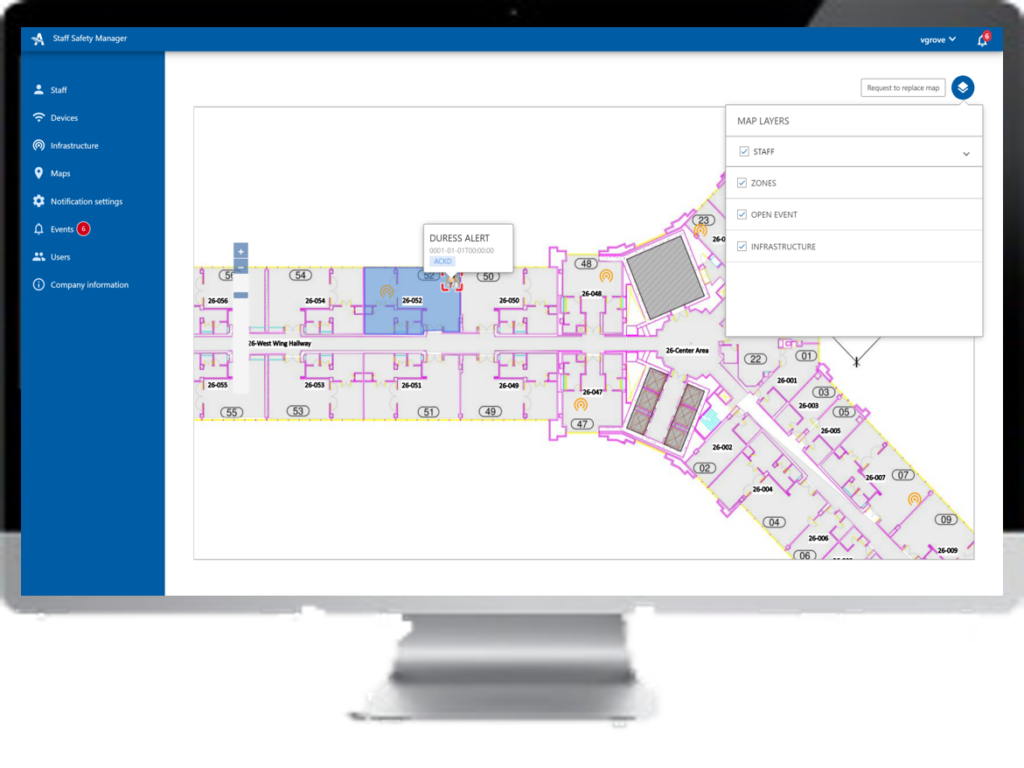
Moreover, the ongoing pandemic has underscored the need for efficient healthcare systems. RTLS could play a pivotal role in infection control by tracking patient and staff interactions, thereby aiding in contact tracing and controlling the spread of infectious diseases within healthcare facilities.
A PubMed study on RTLS in healthcare provides an additional resource for those interested in exploring the empirical evidence supporting these applications and benefits. The study highlights the quantifiable improvements RTLS brings to healthcare settings, reinforcing the technology’s potential to revolutionize how hospitals operate.
RTLS in Manufacturing
At AiRISTA, we have consistently highlighted the transformative impact of Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) across various industries. In the manufacturing sector, RTLS stands as a cornerstone technology, redefining efficiency, productivity, and operational intelligence. This article provides an in-depth look at the applications of RTLS in manufacturing, showcasing its benefits through case studies, examining the unique advantages of BLE as it is nearly as capable as Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology, and discussing future trends.
RTLS technology in manufacturing primarily enhances efficiency and productivity. It achieves this by providing real-time visibility into asset locations, worker movements, and workflow processes. This visibility enables manufacturers to optimize asset utilization, reduce downtime, and streamline production processes. For example, a case study from a large automotive manufacturer showed a significant reduction in search times for tools and equipment post-RTLS implementation, leading to a noticeable increase in production efficiency.
One of the key advances in technologies underpinning RTLS in manufacturing is high-accuracy BLE. With BLE 5.1, angle of arrival (AoA) was introduced which provided submeter accuracy using low-cost BLE tags. Going further, BLE high accuracy distance measurement (HADM) is expected to achieve accuracies below half a meter all using low-power BLE tags. These features allow for precise tracking and positioning, which is critical in applications like smart tooling, inventory tracking, and workforce management.

Looking to the future, the manufacturing industry is set to witness an increased integration of RTLS with other advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and machine learning. This integration will not only enhance the current capabilities of RTLS but also pave the way for predictive analytics and smarter decision-making processes. Manufacturers can anticipate improvements in areas such as predictive maintenance, optimized resource allocation, and enhanced safety protocols.
For those interested in a deeper dive into RTLS applications in manufacturing, ManufacturingTomorrow’s guide on RTLS serves as an excellent resource. It provides comprehensive insights into how RTLS is reshaping manufacturing operations, supported by industry examples and expert opinions.
In conclusion, RTLS technology, especially with the integration of high-accuracy BLE solutions, is rapidly evolving as a game-changer in the manufacturing industry. At AiRISTA Flow, we continue to innovate and provide cutting-edge solutions that harness the power of RTLS, driving the future of manufacturing toward greater efficiency and productivity. Discover more about our industrial solutions at AiRISTA Flow’s Industrial Solutions.
RTLS in Hospitality
In the hospitality industry, Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) are emerging as a vital tool for enhancing guest experiences and streamlining hotel operations. By employing RTLS, hotels and resorts can ensure a seamless, personalized, and efficient service that meets the high expectations of modern guests.
RTLS technology in hospitality primarily focuses on staff safety and improving asset tracking. Guest Room Attendants (GRAs) are often in vulnerable situations and need a simple, low-cost RTLS device to issue an SOS duress event when in trouble. This application is also crucial in a sector where the availability and proper functioning of assets such as cleaning carts, room service trays, and maintenance equipment directly impact guest satisfaction. RTLS enables hotels to track these assets in real time, ensuring they are efficiently utilized and always available where and when needed. This level of operational efficiency not only improves staff productivity but also significantly enhances the guest experience by minimizing delays and service inconsistencies.

A compelling case study in the hospitality sector demonstrates how a prestigious hotel chain used RTLS to improve its operational efficiency. By implementing RTLS, the hotel was able to reduce the time staff spent searching for equipment, streamline housekeeping services, and enhance overall guest satisfaction. The result was an increase in repeat business and positive reviews, showcasing the direct impact of RTLS on both operational performance and guest perception.
For additional insights into RTLS applications in the hospitality industry, visit our RTLS hospitality solutions page. Join us as we delve into various ways RTLS technology can be leveraged to create memorable guest experiences and efficient hotel operations.
RTLS for Enhanced Workplace Safety
Safety in the workplace is paramount, and Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) play a critical role in enhancing safety protocols across various industries. A safe work environment not only protects employees but also improves productivity and maintains high morale. RTLS contributes to workplace safety by providing real-time visibility into the whereabouts of employees, especially in hazardous environments or situations.
One of the primary ways RTLS contributes to safety is through incident response and emergency evacuation. In case of an emergency, such as a fire or chemical spill, RTLS enables quick and efficient evacuation by tracking the real-time location of employees, ensuring that everyone is accounted for and safely evacuated. Additionally, in high-risk environments like manufacturing plants or construction sites, RTLS can be used to monitor workers’ proximity to dangerous areas, alerting them and their supervisors if they enter restricted zones.
Real-world examples of RTLS improving safety are numerous. In a large manufacturing facility, RTLS can be implemented to monitor zones with potential hazards. When an employee enters a hazardous zone, the system sends real-time alerts, preventing potential accidents. Similarly, in healthcare settings, RTLS solutions like those offered by AiRISTA Flow AiRISTA Flow’s Healthcare Personnel Safety Solutions have been instrumental in ensuring the safety of healthcare workers. These solutions enable real-time location tracking of staff, helping in emergencies and reducing response times in critical scenarios.

Another example is in the mining industry, where RTLS can be used to track miners underground. In an emergency, rescuers can quickly locate and reach miners, significantly improving the chances of a successful rescue operation.
In summary, RTLS technology is a crucial component in enhancing workplace safety. By providing real-time visibility and situational awareness, RTLS systems enable proactive safety measures, quick response to emergencies, and ensure overall employee well-being. As industries continue to recognize the importance of workplace safety, the adoption and innovation in RTLS technology are set to rise, making work environments safer and more secure.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) brings with it a set of challenges and considerations that organizations need to address to fully harness the benefits of this technology. One of the primary technical challenges is ensuring accurate and reliable location tracking, especially in complex environments. Factors like signal interference, physical obstructions, and the need for precise indoor tracking can affect the performance of RTLS. Selecting the right combination of technologies (like RFID, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth) and placing infrastructure appropriately are key to overcoming these technical hurdles.
Privacy and security concerns are also paramount when implementing RTLS. Since RTLS involves tracking the movement of individuals and assets, it is crucial to handle this data responsibly to protect individual privacy. This includes establishing clear policies on data usage, obtaining necessary consent, and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR. Additionally, securing the RTLS network against unauthorized access and cyber threats is critical to prevent data breaches and maintain trust in the system.
Integration with existing systems poses another significant challenge. RTLS should seamlessly integrate with an organization’s existing IT infrastructure and software systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). This integration can be complex, requiring careful planning and often custom development to ensure compatibility and data synchronization. Solutions like AiRISTA’s Flow Studio provide a low-code design environment for custom integrations and workflow development.
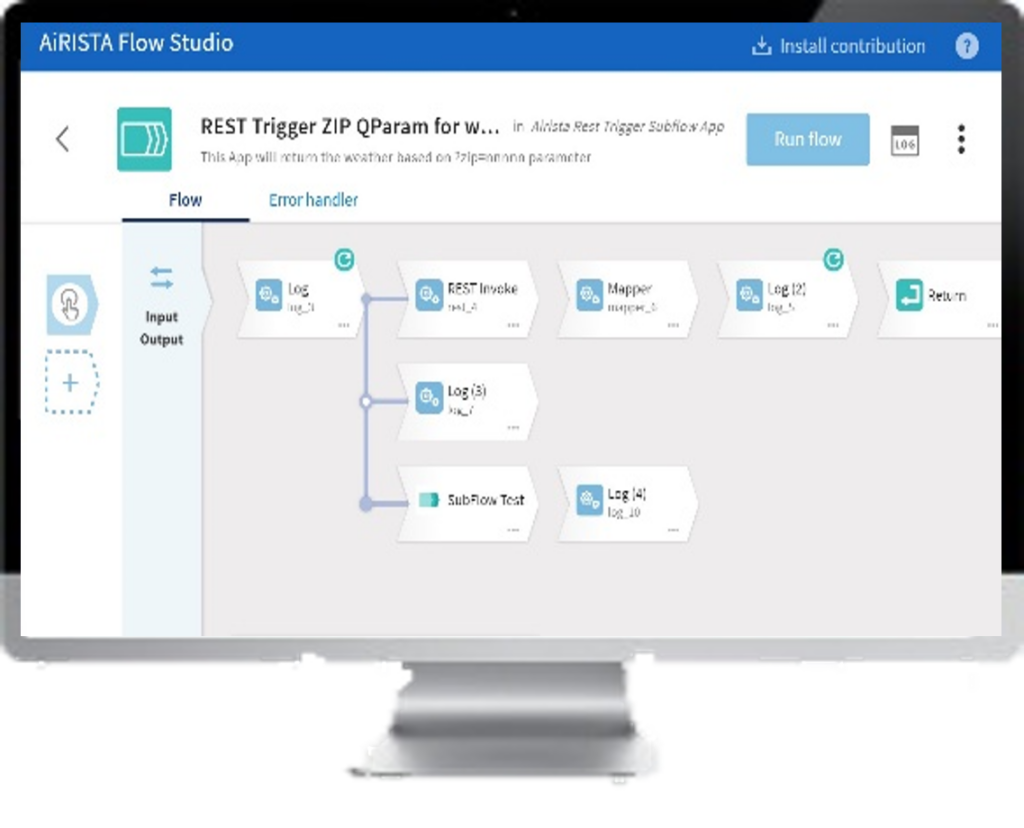
Overcoming these challenges is essential for successful RTLS implementation. It involves careful planning, selection of the right technology, adherence to privacy standards, and effective integration strategies. Addressing these aspects ensures that organizations can leverage RTLS to improve efficiency, safety, and overall operational effectiveness.
The Future of RTLS
The future of Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) is poised for significant advancements, driven by emerging trends and technological innovations. As we look ahead, several key developments are expected to shape the evolution and application of RTLS across various sectors.
One of the major emerging trends is the integration of RTLS with advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Machine Learning (ML). This convergence will enable more intelligent and automated systems capable of predictive analytics, enhanced decision-making, and improved operational efficiency. For instance, integrating RTLS with IoT devices can facilitate automatic environmental adjustments based on the occupancy or usage patterns in smart buildings or manufacturing facilities.
Another trend is the increased accuracy and granularity of location tracking. Advancements in Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology and the development of new algorithms will allow for even more precise tracking, down to the centimeter level. This level of precision will be crucial in applications like automated robotics in manufacturing, patient monitoring in healthcare, and personalized experiences in retail and hospitality.
Future innovations are also expected to focus on the miniaturization and energy efficiency of RTLS hardware. Smaller, more energy-efficient tags and sensors will broaden the scope of RTLS applications, making it feasible to track smaller assets and deploy systems in more diverse environments.
The application of RTLS is set to expand in various sectors. In healthcare, RTLS will play a vital role in patient safety, asset management, and workflow optimization. In manufacturing and logistics, RTLS will continue to enhance supply chain visibility, inventory management, and worker safety. The retail sector will see a growing use of RTLS for customer engagement and inventory tracking, while in smart cities, RTLS will contribute to public safety, urban planning, and resource management.
Additionally, as concerns around privacy and security grow, future RTLS solutions will increasingly incorporate robust security measures and privacy-preserving technologies. This focus will ensure that the benefits of RTLS are realized without compromising individual privacy or data security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) stand as a transformative technology with far-reaching implications across various industries. This article has highlighted the versatility of RTLS, from enhancing operational efficiency in manufacturing to improving patient care in healthcare and ensuring safety in the workplace. Emerging trends like the integration with IoT, AI, and advanced BLE technology point towards a future where RTLS will become even more precise and interconnected. For those considering the adoption of this technology, AiRISTA Flow offers a comprehensive RTLS Buyer’s Guide, which can be an invaluable resource. The potential impact of RTLS is vast, promising not only to optimize current processes but also to open new avenues for innovation and improvement in diverse sectors. As we move forward, RTLS is set to become an integral component of modern operational strategies, driving efficiency, safety, and better decision-making across industries.
FAQ Section
Addressing common questions about RTLS.
Q: How long does a tag’s battery last?
A: Battery consumption is a matter of the radio technology and amount of communication that takes place. Wi-Fi for example takes a heavier toll on batteries than Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). The communication requirements of a tag vary by use case. For example, to track a Wi-Fi tag that updates every 3 seconds might require recharging every couple of days. On the other hand, a BLE tag that chirps every couple of minutes might last 5 or more years.
Q: How much do RTLS tags cost?
A: Thanks to the consumerization of BLE chips, a simple BLE tag can cost several dollars ($US). Tags that support multiple radio technologies and types of interfaces can cost upward of $100.
Q: What accuracy can I expect with an RTLS solution?
A: Using the wireless access points in your environment and Wi-Fi tags, you can expect roughly 5-7 meters of accuracy. AiRISTA improves on this using a radio frequency (RF) fingerprinting technique that increases accuracy to 3-5 meters. Augmenting the access points with small radios installed nearer the tags will improve accuracy to under 3 meters. New BLE technology, like the angle of arrival, has been introduced which provides submeter accuracy.
Q: Can RTLS track tags in the vertical dimension?
A: Newer technology like BLE angle of arrival has the additional benefit of being able to track tags in the X, Y, and Z dimensions.
Q: What is the difference between location and proximity?
A: Location provides a position on a map (think of an X, Y coordinate). This is useful when you want to know where within an area a tag is. Location is determined when 3 or more reference points like access points detect the tag. Algorithms using triangulation are used to determine the position. Proximity is simply a measure of how near a tag is to a device like an access point or other detector. Since there is only one device detecting the tag, there is no sense of left, right, forward, or back. Proximity is useful for detecting when a tag passes a specific spot like a doorway.
Q: What is the role of the RTLS software platform?
A: Analysts like Gartner encourage customers to consider the ability of the RTLS software solution to provide a platform for location insights across the enterprise. The RTLS software platform collects signal information from hundreds and thousands of tags. Using that information, it uses a number of algorithms to determine each tag’s location. The software manages the maps on which the locations are positioned. The platform facilitates rules that alert to changes in the locations and conditions of tags. But to be a true platform, the software needs to scale across the enterprise, not only in terms of compute capability but in terms of its support for a wide range of use cases. As a platform, it must also support a broad range of technologies that apply the right level of location accuracy at an appropriate cost. Finally, to derive the most value from the RTLS platform the software must readily integrate with the other applications in the enterprise that drive workflows and continuous operation.
Q: What are the pros and cons of RFID and RTLS?
A: RFID tags are typically a couple $USD or less and require no batteries. However to be energized they require “RFID readers” positioned nearby. The location of each reader is used to infer the location of the tag. The readers typically provide proximity and are positioned at choke points like doorways. RTLS, on the other hand, uses tags that cost under $10 USD to over $100 depending on the sophistication. Battery maintenance should be considered. RTLS solutions provide a near continuous x,y position in near real time.





